Phenylephrine Response in Upper Eyelid Ptosis
Contributors: Kelly H. Yom, BA; Aaron M. Ricca, MD; Audrey C. Ko, MD
Photographer: Audrey C. Ko, MD
Posted July 31, 2018
In patients with mild to moderate upper eyelid ptosis, phenylephrine eyedrops are used to assess whether ptosis correction is achievable with a Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection (MMCR). As an alpha-adrenergic agonist, phenylephrine stimulates the sympathetically innervated Müller's muscle when applied topically. The resulting smooth muscle contraction predicts the potential eyelid lift possible with an MMCR – usually ≤ 3 mm.1 It is estimated that 73 – 78% of patients presenting with ptosis will respond desirably to phenylephrine testing and, thus, will be excellent candidates for MMCR.2, 3 A ptotic upper eyelid that does not sufficiently elevate in response to phenylephrine testing indicates an alternative ptosis correction technique, such as a levator advancement or a frontalis suspension, should be considered.
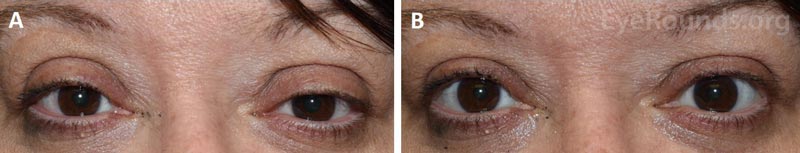
Figure 1. External photographs of a female patient before and after phenylephrine testing. A. Bilateral upper eyelid ptosis is evident prior to phenylephrine testing. B. Elevation of both upper eyelids is demonstrated ten minutes after administration of phenylephrine eye drops in both eyes.
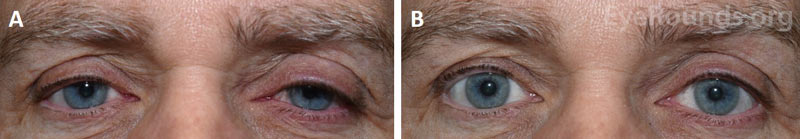
Figure 2. External photographs of a male patient before and after phenylephrine testing. A. Bilateral upper eyelid ptosis is evident prior to phenylephrine testing. B. Elevation of both upper eyelids is demonstrated ten minutes after administration of phenylephrine eye drops in both eyes.
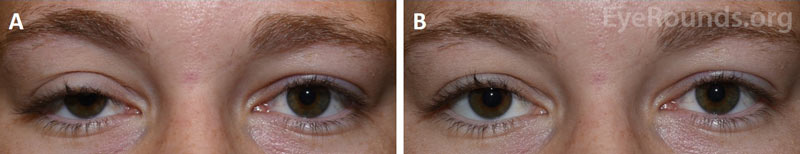
Figure 3. External photographs of a unilateral eyelid ptosis before and after phenylephrine testing. Photos before (A) and ten minutes after (B) administration of phenylephrine eye drops in the right eye only demonstrate the marked elevation of the right eyelid above the pupillary light reflex after drop administration.
References
- Ben Simon GJ, Lee S, Schwarcz RM, McCann JD, Goldberg RA. Muller's muscle-conjunctival resection for correction of upper eyelid ptosis: relationship between phenylephrine testing and the amount of tissue resected with final eyelid position. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2007;9(6):413-417. https://PubMed.gov/18025352. DOI: 10.1001/archfaci.9.6.413
- Barsegian A, Botwinick A, Reddy HS. The Phenylephrine Test Revisited. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2018;34(2):151-154. https://PubMed.gov/28353471. DOI: 10.1097/iop.0000000000000903
- Grace Lee N, Lin LW, Mehta S, Freitag SK. Response to phenylephrine testing in upper eyelids with ptosis. Digit J Ophthalmol 2015;21(3):1-12. https://PubMed.gov/27330465. DOI: 10.5693/djo.01.2015.05.001

Ophthalmic Atlas Images by EyeRounds.org, The University of Iowa are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.