
The University of Iowa
Department of Neurology and Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences
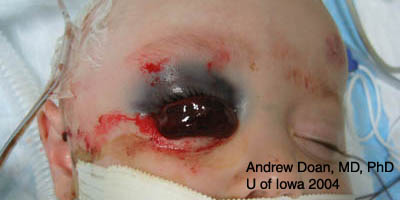
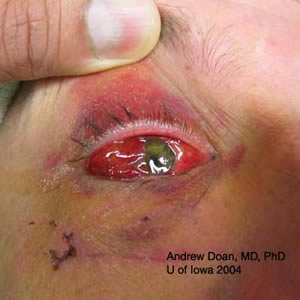
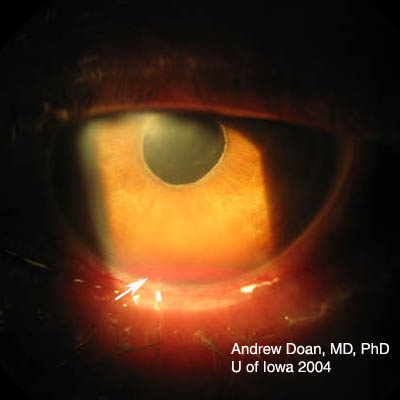
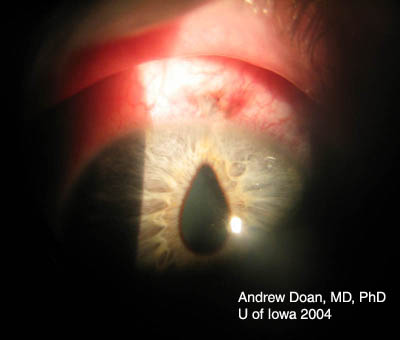

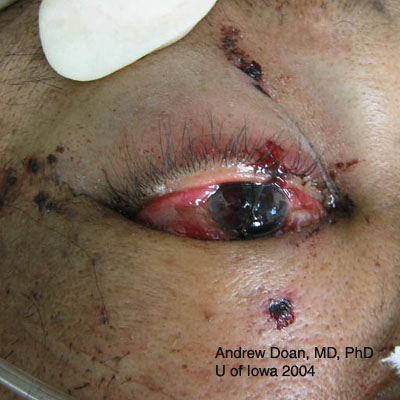
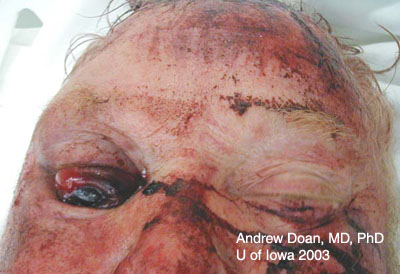
| Repair | Suture |
|---|---|
| Cornea | 10-0 Nylon on spatulated needle |
| Sclera | 9-0 or 8-0 Nylon on spatulated needle |
| Conjunctiva | 7-0 Vicryl |
| Medial canthal tendon | 4-0 Mersiline |
| Skin | 5-0 Fast Absorbing Gut (preferred at Iowa), 7-0 Vicryl or 6-0 Silk |
| Lid margin | 4-0 Silk through tarsal plate + 6-0 Silk for skin -OR- 5-0 Vicryl through tarsal plate and two 7-0 Vicryl sutures for lid margin (vertical matress) and skin |
| Canalicular laceration | Stent with silicone tubing (leave for 6 months) 6-0 Chromic and 6-0 Silk sutures |
| Type of Fracture… | Look for… |
|---|---|
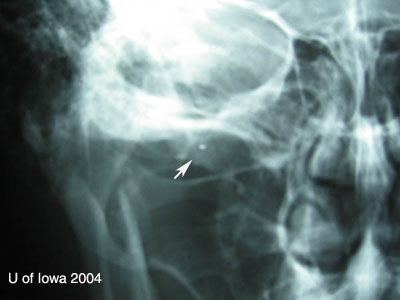
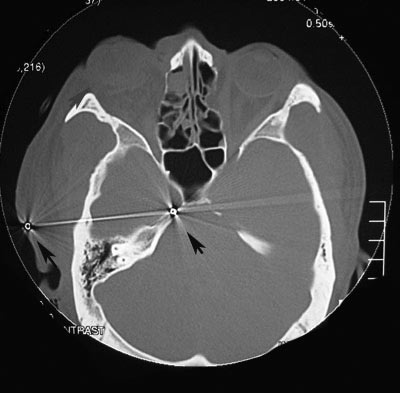
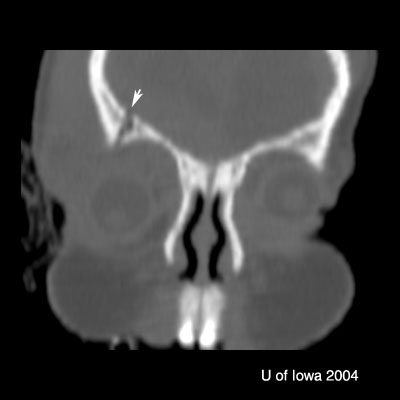
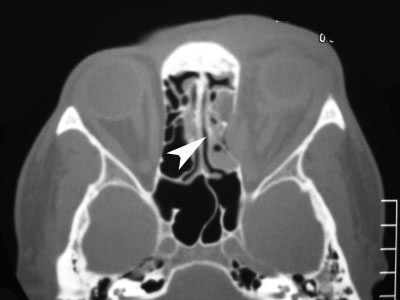
| Le Fort II-III | Optic canal and nasal lacrimal duct injury |
| Orbital floor fracture | Vertical diplopia, extraocular muscle rounding on CT, V2 hypoesthesia, orbital/sub-cutaneous emphysema, enophthalmos, oculocardiac reflex, pupil abnormalities |
| Medial wall fracture (orbit) | Horizontal diplopia, orbital emphysema, orbital hemorrhage, enophthalmos |
| Roof fracture (orbit) | Restricted upgaze, ptosis, epistaxis, CSF rhinorrhea, anosmia, depression of superior rim, V1 hypoesthesia, hypo-ophthalmos, pulsatile exophthalmos; traumatic optic neuropathy |
| ZMC Fracture | Point tenderness, ecchymosis, malar flattening, lateral canthal downward displacement, V2 hypoesthesia, trismus, malocclusion of jaw, inferior or lateral rim step-off. |
| NOE (Nasal-Orbital-Ethmoid) Fracture | Facial flattening, telecanthus, epistaxis, CSF rhinorrhea, anosmia, nasolacrimal duct damage, optic canal damage |
The most common local anesthetic mixture is 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine to provide some hemostasis. Addition of 0.5% bupivacaine will provide longer anesthesia for lengthy procedures. The following diagrams illustrate common local nerve blocks used in ophthalmology.
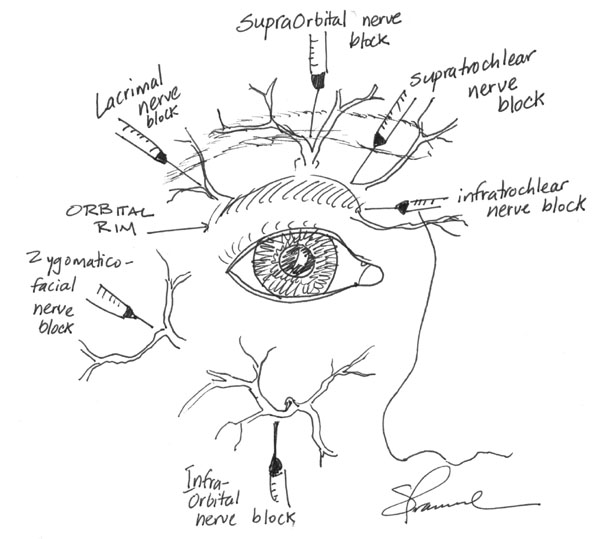
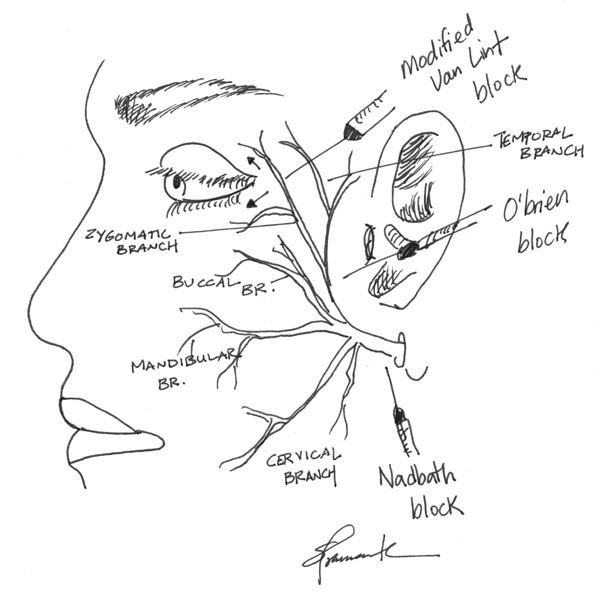
Retrobulbar blocks are useful methods of achieving anesthesia for intraocular and orbital surgeries. Blocks are good alternatives to general anesthesia when general anesthesia is undesireable or contraindicated.
There are many techniques to adminster a retrobulbar block. The method described here is what I prefer. Depending on the type of anesthetic, a block may last over four hours with a mixture of lidocaine 1% and bupivacaine 0.375%.
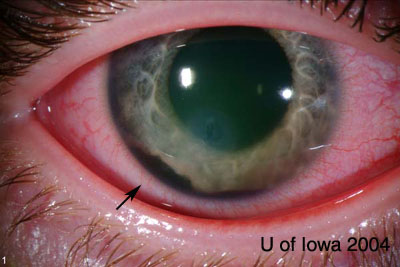
Base injuries are more worrisome as they can penetrate deeper into ocular tissue. Grading of corneal burns is based on extent of limbal ischemia, which indicates loss of corneal epithelial stem cells, and degree of corneal haze obscurring iris details.
Grade 1 (Very good prognosis)
|
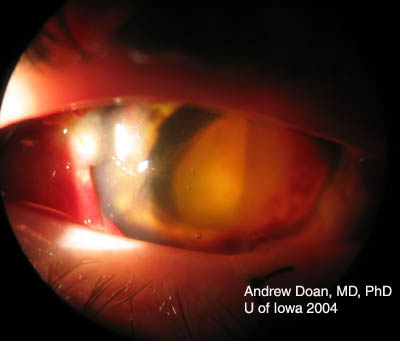
Grade 2 (Good prognosis)
|
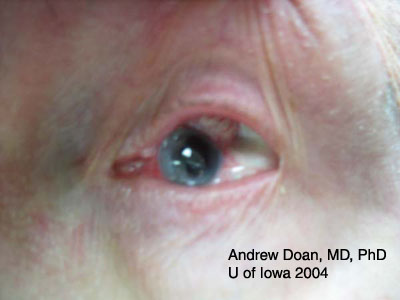
Grade 3 (Guarded prognosis)
|
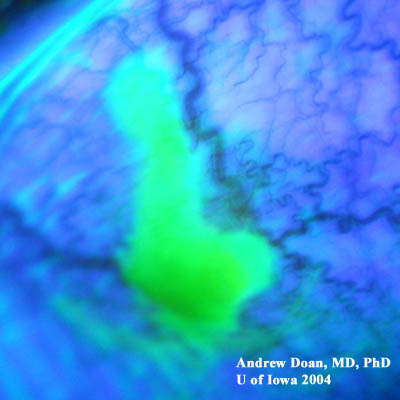
Grade 4 (Poor prognosis)
|
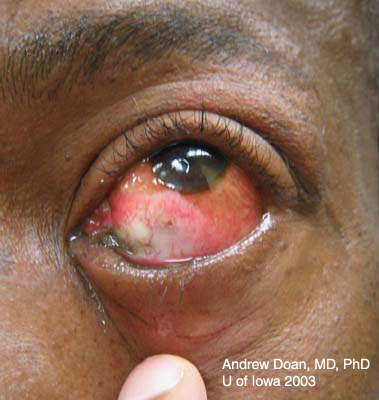
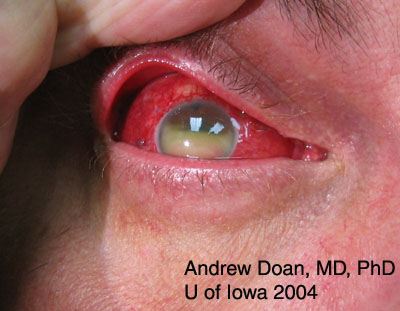
Grading helps to determine the aggressiveness and course of treatment. Treatment modalities include some or all of the following depending on the severity of the burn:
The Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study (EVS) [2] applies only to post-cataract endophthalmitis. The study states that patients did better with a vitrectomy and injection of intravitreal antibiotics when the vision is light perception or worse. If vision is hand motions or better, then patients with a TAP (vitreous biopsy and culture) and intravitreal injection of antibiotics did as well as patients who had a vitrectomy and injection of intravitreal antibiotics.
If referral doctor suspects endophthalmitis, ask about penicillin allergy before patient is enroute.