
This 87-year-old male has alongstanding history of primary open angle glaucoma. His optic nerve is significantly cupped with a marked number of optociliary shunt vessels. There are several drusen in the peripapillary region.
Optociliary shunt vessels are collateral vessels connecting the choroidal and the retinal vasculature. The differential diagnosis for acquired optociliary shunt vessels commonly includes central retinal vein occlusion, chronic glaucoma, chronic papilledema, or an optic nerve sheath meningioma. Optociliary shunt vessels can be differentiated from neovascularization of the disc by their large caliber and lack of leakage on fluorescein angiogram.
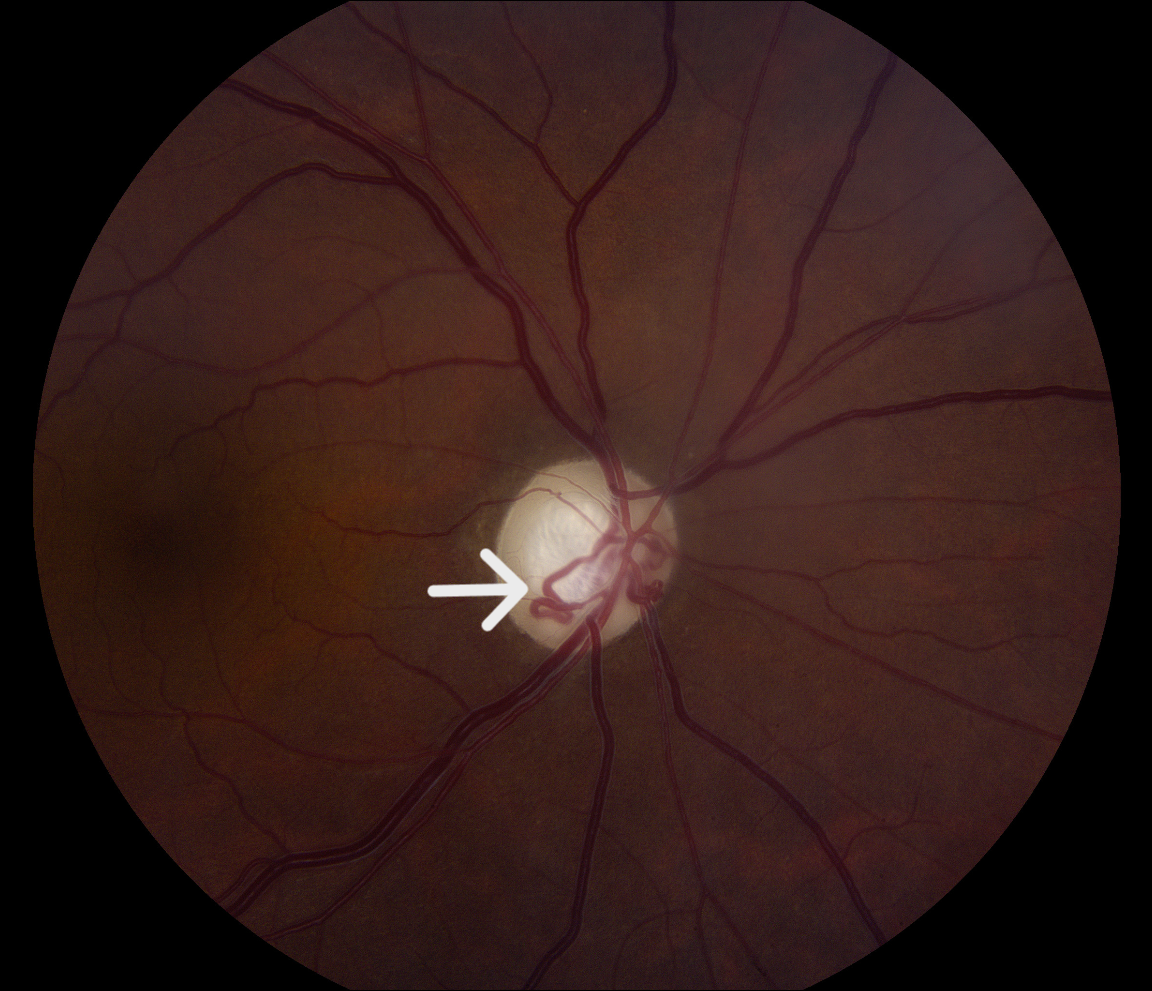
This 60-year-old male patient has a history of severe glaucoma. Fundus photos show large optic discs with large deep cups and pallor of the neuroretinal rim bilaterally. Optociliary shunt vessels are present (white arrows). These are also known as retinochoroidal venous collaterals since they are collateral vessels that connect the retinal and choroidal circulation in cases of long-standing retinal venous congestion. The differential diagnosis for acquired optociliary shunt vessels commonly includes central retinal vein occlusion, chronic glaucoma, chronic papilledema, or an optic nerve sheath meningioma.

Ophthalmic Atlas Images by EyeRounds.org, The University of Iowa are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.