
69-year-old female referred by an outside retina specialist for a recurrent macula-off retinal detachment in the right eye. She was previously treated for a macula-off retinal detachment in the right eye 1.5 months prior to presentation with surgery. She had gradual vision loss over the prior few months. No falls or trauma. No other eye surgeries. No family history of retinal detachments.
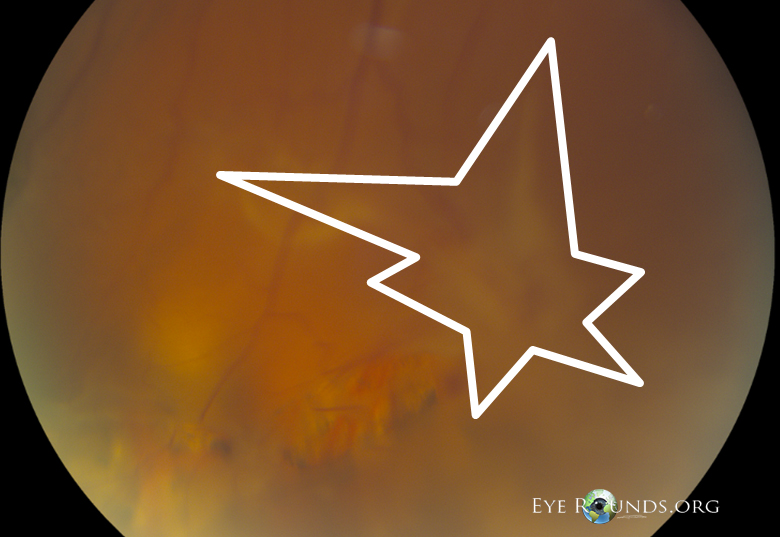

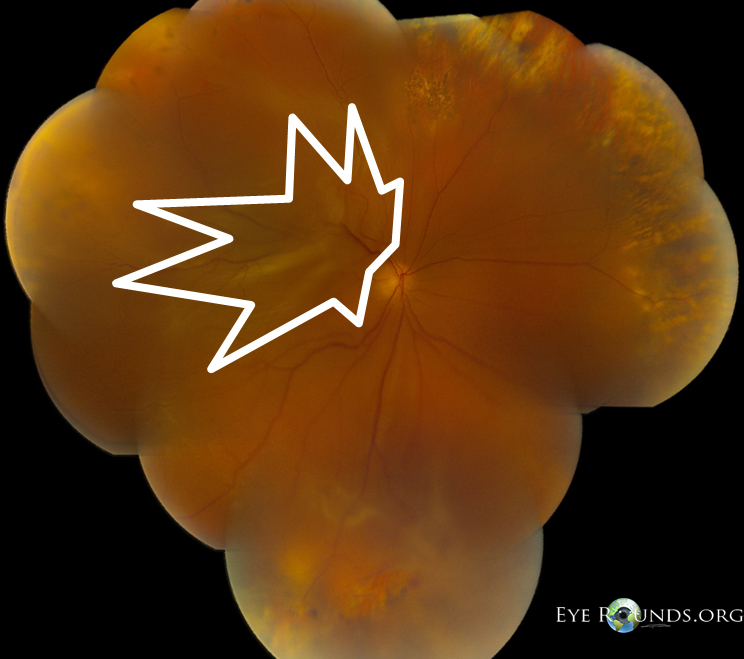
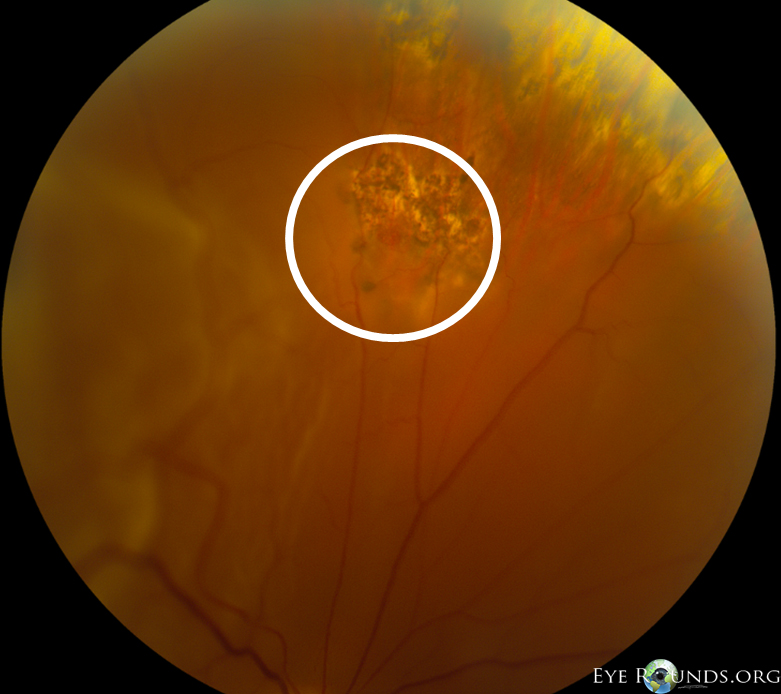
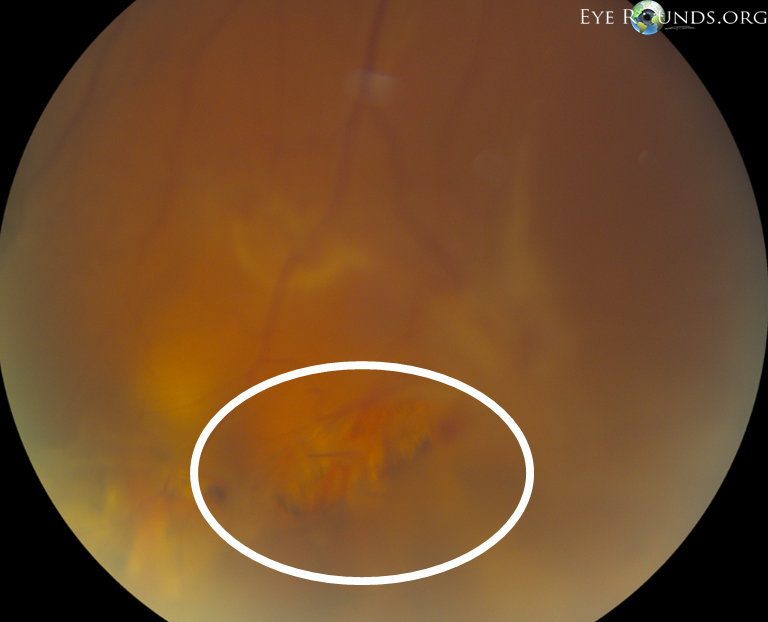

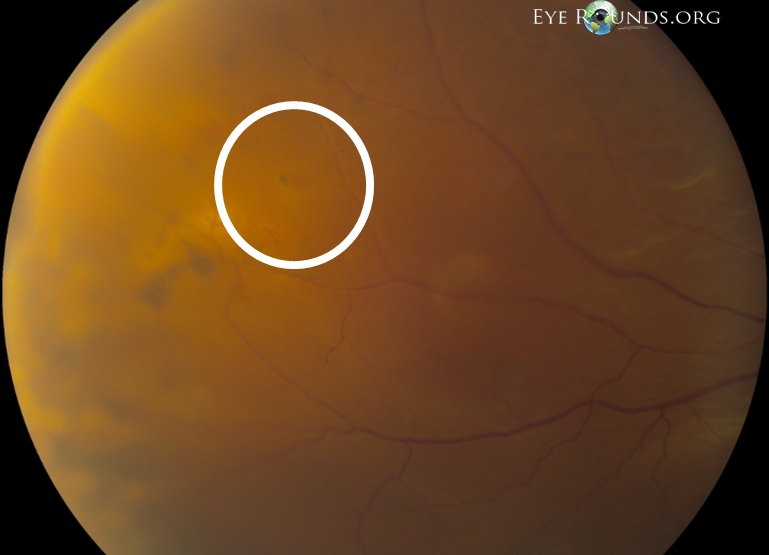
Patient underwent elective 23-gauge pars plana vitrectomy, scleral buckle, and silicone oil placement in the right eye.
| Grade | Name | Clinical Sign |
|---|---|---|
| A | Minimal | Vitreous haze, vitreous pigment clumps |
| B | Moderate | Wrinkling of inner retinal surface, rolled edge of retinal break, retinal stiffness, vessel tortuosity |
| C | Marked |
Full-thickness fixed retinal folds C-1 one quadrant C-2 two quadrants C-3 three quadrants |
| D | Massive |
Fixed retinal folds in four quadrants D-1 wide funnel shape D-2 narrow funnel shape D-2 closed funnel (optic nerve head not visible) |
| Grade | Features |
|---|---|
| A | Vitreous haze, vitreous pigment clumps, pigment clusters on inferior retinal |
| B | Wrinkling of inner retinal surface, retinal stiffness, vessel tortuosity, rolled and irregular edge of retinal break, decreased mobility of vitreous |
| CP1-12* | Posterior to equator: focal, diffuse, or circumferential full-thickness folds, subretinal strands |
| CA1-12* | Anterior to equator: focal, diffuse, or circumferential full-thickness folds, subretinal strands, anterior displacement, condensed vitreous with strands |
| Type | Location in Relation to Equator | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Focal | Posterior | Star folds posterior to vitreous base |
| Diffuse | Posterior | Confluent star folds posterior to vitreous base: optic disc may not be visible |
| Subretinal | Posterior/anterior | Proliferations under retina: annular strand near disc, linear strands, moth-eaten-appearing sheets |
| Circumferential | Anterior | Contraction along posterior edge of vitreous base with central displacement of retina, peripheral retina stretched, posterior retina in radial folds |
| Anterior displacement | Anterior | Vitreous base pulled anteriorly by proliferative tissue, peripheral retina trough, ciliary processes may be stretched and may be covered by membrane, iris may be retracted |

Ophthalmic Atlas Images by EyeRounds.org, The University of Iowa are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.