Chief Complaint: Male patient with painful, red, tearing right eye (OD) after fourth corneal transplant.
History of Present Illness: 82-year-old male with complicated ocular history presented with painful, red, tearing right eye of one month’s duration. Pain was described as a foreign body sensation associated with yellow-colored discharge. His vision had been stable at hand motions. Patient has a history of multiple corneal transplant failures in his right eye. His initial transplant was performed due to pseudophakic corneal edema, which occurred 10 years after cataract surgery. He then developed an infection in the graft, which resulted in a perforation, requiring emergent repeat corneal transplantation. He then underwent two subsequent graft failures resulting in his third and fourth corneal transplants.
Past Ocular History:
Medical History: Four vessel cardiac bypass surgery 2005, Hypertension, Hypercholesterolemia
Medications: Ocular medications included latanoprost at night OU. Systemic medications included Aspirin, Atenolol, Atorvastatin, Calcium carbonate, Clopidogrel, Ezetimibe, Pantoprazole.
Family History: Noncontributory
Social History: Two alcoholic beverages per day. Patient is a non-smoker.
Ocular Examination:
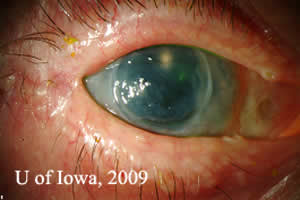
Course: Patient was diagnosed with MRSA keratitis and treated with fortified antibiotic drops including Vancomycin 25mg/ml 1 drop every hour and Tobramycin 14mg/ml 1 drop every hour for two days and then switched to gatifloxacin 1 drop 4 times per day. The infiltrate resolved, however the patient developed a persistent epithelial defect. This was treated with a bandage contact lens, lubricating eye drops, and an antibiotic drop. There was suspicion at this point for neurotrophic keratitis. The patient underwent permanent tarsorrhaphy to try to heal the epithelial defect, however the tarsorrhaphy dehisced and had to be revised. Eventually the epithelial defect healed, but after 4 months, he once again presented with a persistent epithelial defect and endothelial graft failure (see Figure 1).
| Figure 1A: Persistent epithelial defect, edematous failed corneal graft, and limbal stem cell deficiency. Note permanent tarsorrhaphy at lateral canthus. | Figure 1: Irregular corneal surface and thinning of anterior corneal stroma, illustrated by thin beam illumination . |
 |
 |
Management options at this time included conservative management with an attempt to heal the persistent epithelial defect with a bandage contact lens. However due to the degree of corneal thinning already present, this option would place the patient at risk for future perforation. Other options would include surface phototherapeutic keratectomy. Once again, due to the amount of stromal thinning, this was not a good option. Another option would be to perform an amniotic membrane graft or Gundersen conjunctival flap to attempt to heal the epithelial defect but these options completely obstruct vision. Repeat corneal transplantation was another viable option, however, certain risk factors exist that worsen prognosis for grafts, including multiple previously failed corneal transplants, neurotrophic keratitis, inflammatory ocular surface disease, and limbal stem cell deficiency. Due to the patient’s amount of corneal thinning, desire for improved vision, and his good vision potential if his ocular surface could be improved (combined with the patient’s high risk of repeat corneal transplant failure) the patient underwent a Boston Type 1 Keratoprosthesis (See Video 1).
Video 1: Boston Type 1 Keratoprosthesis surgery. The patient was refracted to a visual acuity of 20/40 within the first month post-operatively.
If video fails to load, use this link: https://vimeo.com/134676714
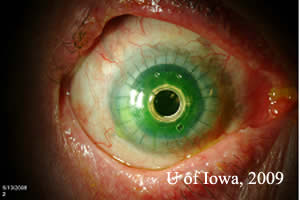
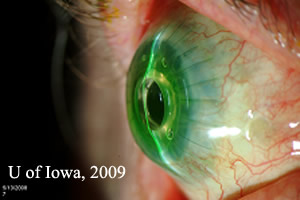
Post operatively the patient was started on Prednisolone acetate twice daily to prevent rejection. He was also placed on Medroxyprogesterone drops twice daily and oral Doxycyline 100 milligrams daily to prevent corneal melting. To prevent infection, Vancomycin 1 drop of 16 mg/ml daily and gatifloxacin twice daily were initiated. A soft contact lens was placed to prevent surface breakdown. Post-operatively, his visual acuity improved with pinhole to 20/40. He was followed closely over a period of six months and at his last visit, his visual acuity was maintained at 20/40, the keratoprosthesis remained clear, and his cornea showed no signs of thinning (see Figure 2).
| Figure 2A:Post-operative appearance of Boston KPro. | Figure 2B:Note contour of Boston Kpro on thin beam illumination. |
 |
 |
| Figure 2C: Note holes in back plate on retroillumination. | Figure 2D: Highlight of prosthesis contour. |
 |
 |
History of Keratoprosthesis: More than 40,000 corneal transplants are performed per year in the United States for diseases such as pseudophakic bullous keratopathy, aphakic bullous keratopathy, trauma, infections, and corneal dystrophies or ectasias. Corneal transplants have a very high success rate in initial grafts, with reports of greater than 95% remaining clear over a period of four and ten years (8). Other studies have reported failure rates of between 9% and 30% over a three to ten year period (2, 6, 10, 11, 14). However, the prognosis for subsequent graft failure is worse. In analyzing data on all corneal transplants performed for any indication in patients with initial corneal transplant versus repeat corneal transplants, Bersudsky et al. determined that survival rates for first time repeat grafts were 55% at 3.5 years, and 28% at 4.5 years. Second time regrafts had survival rates of 45% at 3.5 years and 20% at 4.5 years (1). This is not to say that once a graft has failed once, a repeat graft has an estimated 50% chance of failure. Consideration has to be taken into account as to the reason for failure. High risk factors for regraft failure include glaucoma, ocular surface disease and inflammation, limbal stem cell deficiency, and history of multiple ocular surgeries (13).
Because of the high risk of regraft failure in some patients, keratoprosthesis (artificial corneas) have been designed to provide a clear corneal window in patients with severe corneal opacification and corneal blindness. The concept of an artificial cornea is not novel. First suggested by Dr. Pellier de Quengsy, a French ophthalmologist in 1789, artificial corneas have undergone investigation for over two centuries and included design materials such as glass, plastics, hydrogels, and even tooth dentin (3, 5, 7).
There are currently two artificial corneas approved for use in the United States , the AlphaCor® artificial cornea and the Dohlman-Doane or Boston Keratoprosthesis (Boston KPro). For a discussion on the AlphaCor® artificial cornea, please review the EyeRounds case entitled The Evolution of Surgical Approaches to AlphaCor® Keratoprosthesis: Insertion and Associated Complications.
The Boston KPro was first described in 1974 by Dohlman et al., however, it failed to gain popularity at that time due to complications and imperfections in design (4). The device was approved by the FDA for use in the United States in 1992. Reports from the literature support high success rates based on visual acuity outcomes and retention rates of the device. The Multicenter Boston Type 1 Keratoprosthesis Study (MBTKS), a prospective case series of 141 cases from 17 centers with an average follow up of 8.5 months, report retention rates of 95% with visual acuity outcomes of greater than 20/40 in 23% of patients and greater than 20/200 in 57% of patients. Failure for visual acuity to improve from the Boston Keratoprosthesis was attributed to underlying ocular disease such as advanced glaucoma, macular degeneration, or retinal detachment (15).
Design: Type I KPro is made of a 5.5 to 7.0 millimeter central rigid polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) optic/front plate whose refractive power can be selected based on axial eye length and phakic vs aphakic status of the patient. This front plate also has a 3.5 mm stem that connects to a 7.0 mm in diameter back plate also made of PMMA. The back plate has 16 holes to facilitate direct communication with the aqueous for nutrition and hydration of the cornea. The donor corneal tissue is placed between the front plate and the back plate, with the plate being snapped or screwed onto the stem (newer designs are threadless and can be snapped together). The whole assembly is locked together with a titanium locking ring. The anterior-posterior length of the whole assembly is 3.7 mm, allowing or a visual field of 60 degrees (5). The whole assembly can then be suture to the recipient eye like a typical corneal transplant as demonstrated in Video 1. The Boston Type II KPro is similar in design to the Type I, however, this design is used only for patients with severe ocular surface disease where there are no fornices to support the device. This design has a 2 mm long anterior nub off the front plate which penetrates skin or buccal mucosa (5).
Post-operative management: Boston KPro patients need close post-surgical follow up. These patients, due to the evaporative forces on the cornea induced by the irregular shape and material of the prosthesis (See Figure 2) are at risk for epithelial defects, stromal thinning, and dellen formation. It is routine practice at the University of Iowa to prescribe a therapeutic soft contact lens to be worn daily to maintain a healthy, less evaporative surface. These patients are also treated with oral doxycyline and topical medroxyprogesterone to prevent stromal melting, as well as topical prednisolone acetate to prevent rejection. Before the routine use of daily vancomycin drops, high incidences of bacterial endophthalmitis from gram positive cocci were reported (9). Khan et al. reports no cases of bacterial endophthalmitis over a period of six years when the following utilizing prophylactic Vancomycin drops (7).
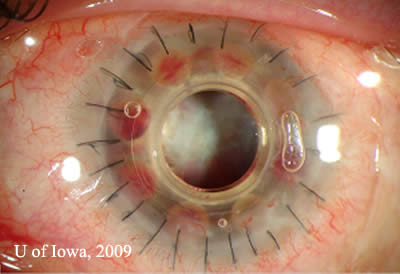
Complications: Retroprosthetic membranes (RPM) are one of the most common complications of the Boston KPro (See Figure 4). According to the MBTKS, 25% of cases developed RPM, most of which did not need to be treated. If treatment was required, the majority could be treated with Nd:YAG membrantomy. A few cases required surgical membranectomy (15). The histopathology of RPMs are of avascular fibrous tissue representing corneal stromal downgrowth over the stem of the device onto the backplate (12).
 |
Another feared complication of the keratoprosthesis is retinal detachment. The MBTKS data revealed 5 cases of retinal detachment out of 141 cases reviewed (3.5%) (15). This number is much lower than previously reported data from Ma et al, who revealed 12% of the 110 cases reviewed resulted in retinal detachment (8).
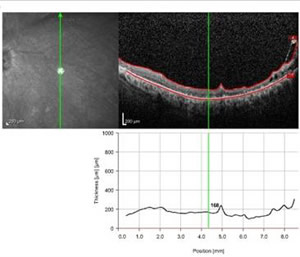
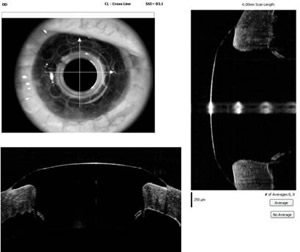
Many patients with keratoprosthesis either have glaucoma prior to surgery or develop glaucoma after the Boston KPro. Data from the MBTKS revealed that 52% of eyes had glaucoma prior to their Boston KPro, and of those with glaucoma, 53% had tubes and 11% had a prior trabeculectomy. After the Boston KPro, 21 eyes developed elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), with 11 of these eyes requiring tubes (15). Once the Boston KPro is in place, measuring IOP is difficult. Measurements taken over the prosthetic will be markedly elevated and measurements taken over the sclera are not very accurate. Glaucoma for these patients must be followed using visual fields. Spectral domain posterior segment optical coherence tomography (OCT) may be useful in following the status of the optic nerve in the absence of accurate intraocular pressure measurements. In addition, time domain and spectral domain anterior segment OCT may be useful in documenting stability of the device around the stem (See Figure 5).
| Figure 5A:Spectral domain posterior segment OCT showing the macula in a patient with a Boston KPro | Figure 5B: Spectral domain anterior segment OCT showing the anterior chamber of a patient with a Boston KPro |
 |
 |
4. Dohlman CH, Schneider HA, Doane MG. Prosthokeratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974;77:694-700.
Birkholz ES, Goins KM. Boston Keratoprosthesis: An option for patients with multiple failed corneal grafts. March 9, 2009; Available from: http://www.EyeRounds.org/cases/94-Boston-Keratoprosthesis-Failed-Corneal-Graft.htm.

Ophthalmic Atlas Images by EyeRounds.org, The University of Iowa are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.