Idiopathic Intracranial
Hypertension
(Pseudotumor Cerebri)
Michael Wall, M.D.
The University of Iowa
Department of Neurology and
Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences
How is the diagnosis of IIH made?
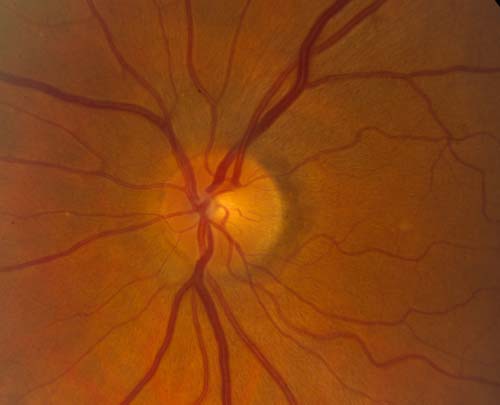
The diagnosis of IIH is made by identifying the typical symptoms of the disease along with documentation of a high spinal fluid pressure (measured during a spinal tap). The neurologic examination is normal except for the presence of swollen optic nerves called papilledema (seen by examining the back of the eye). (Figs 3-8) Sometimes double vision occurs, caused by limitation of lateral eye movement. Lastly, neuroimaging procedures such as CT scans or MRI scanning are normal except for signs known to occur with increased pressure.
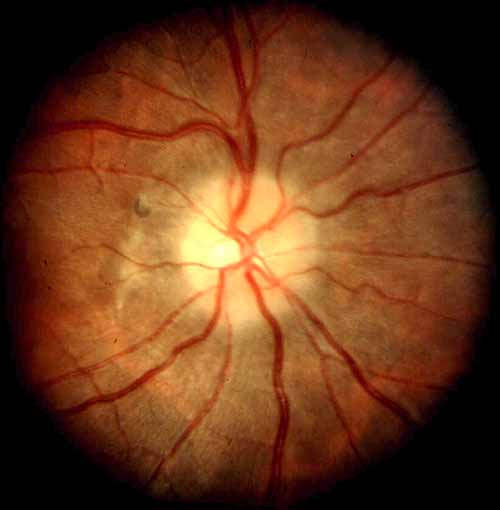
Figure 4. An optic nerve with mild swelling
(papilledema).
Note the pathologic"C"-shaped halo of edema surrounding the
optic disk (Grade I papilledema).
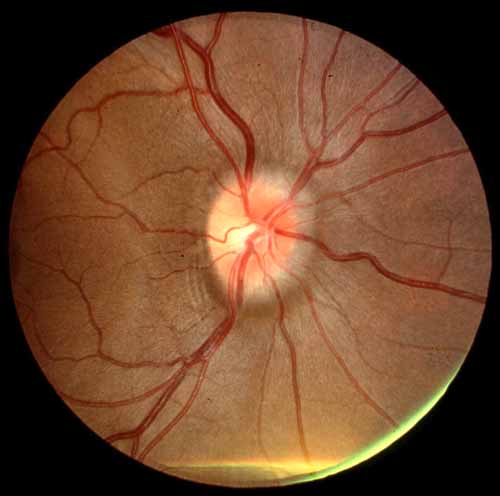
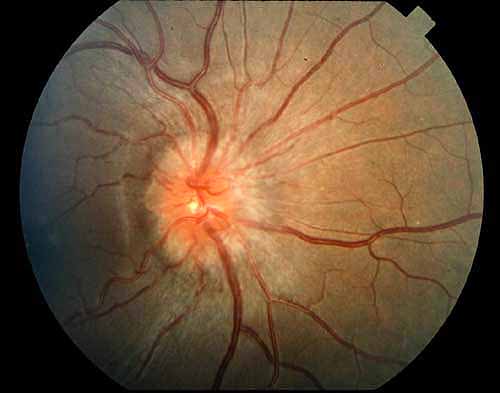
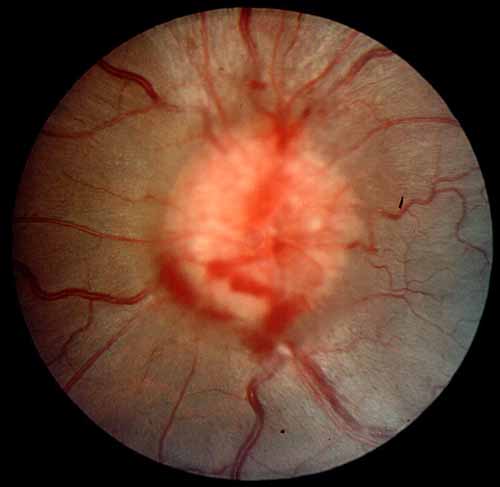
A subretinal hemorrhage is present at 7 o'clock.
Continue with What is the relationship between
optic nerve swelling and visual loss?
Return to IIH Index